May 23, 2024
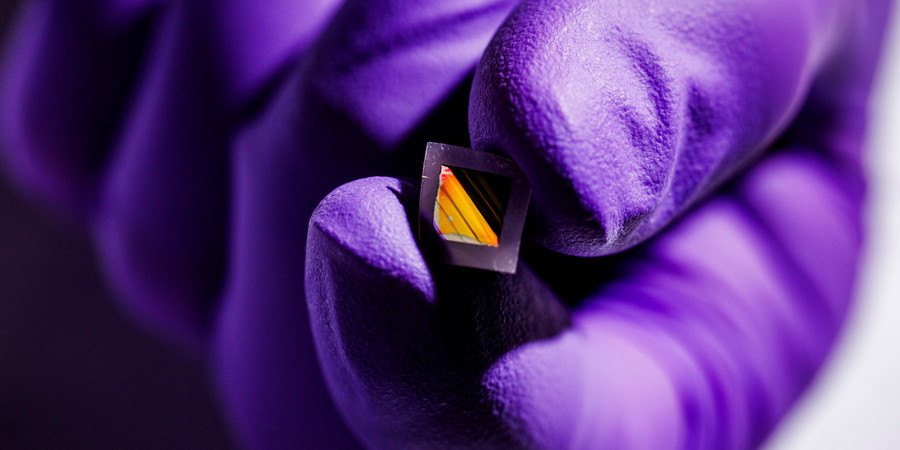
The scorching surface of Venus, where temperatures can climb to 480 degrees Celsius (hot enough to melt lead), is an inhospitable place for humans and machines alike. One reason scientists have not yet been able to send a rover to the planet’s surface is because silicon-based electronics can’t operate in such extreme temperatures for an extended period of time.
For high-temperature applications like Venus exploration, researchers have recently turned to gallium nitride, a unique material that can withstand temperatures of 500 degrees or more.
The material is already used in some terrestrial electronics, like phone chargers and cell phone towers, but scientists don’t have a good grasp of how gallium nitride devices would behave at temperatures beyond 300 degrees, which is the operational limit of conventional silicon electronics.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
III-Nitride Ferroelectrics for Integrated Low-Power and Extreme-Environment Memory
Monday, May 5, 2025 | 4:00 - 5:00pm ET
Hybrid
Zoom & MIT Campus
New Electronic “skin” could Enable Lightweight Night-vision Glasses
Jennifer Chu | MIT News
MIT engineers developed ultrathin electronic films that sense heat and other signals, and could reduce the bulk of conventional goggles and scopes.
MIT Engineers Print Synthetic “Metamaterials” that are Both Strong and Stretchy
Jennifer Chu | MIT News
A new method could enable stretchable ceramics, glass, and metals, for tear-proof textiles or stretchy semiconductors.