Dina Genkina | IEEE Spectrum
December 02, 2022
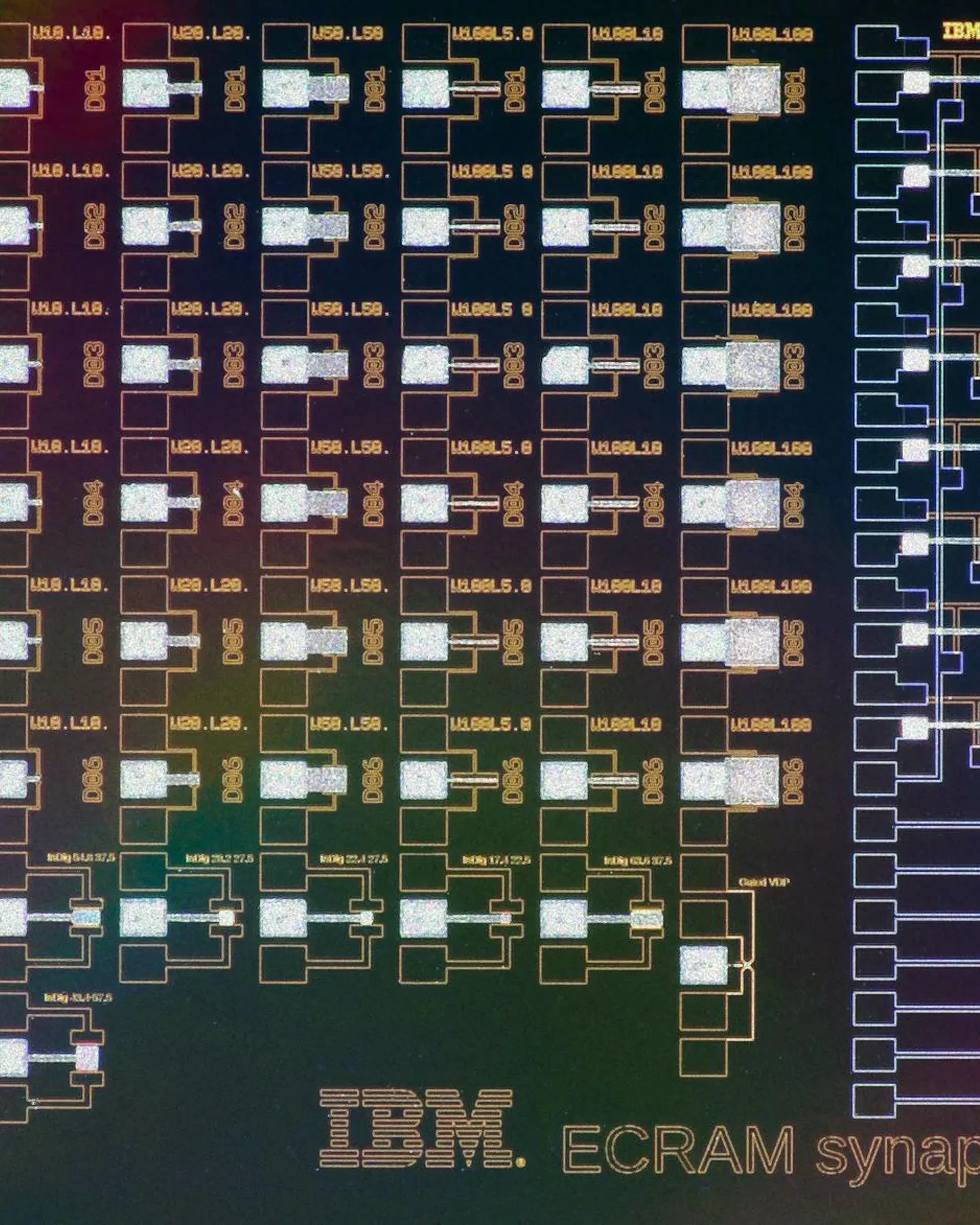
How far away could an artificial brain be? Perhaps a very long way off still, but a working analogue to the essential element of the brain’s networks, the synapse, appears closer at hand now.
That’s because a device that draws inspiration from batteries now appears surprisingly well suited to run artificial neural networks. Called electrochemical RAM (ECRAM), it is giving traditional transistor-based AI an unexpected run for its money—and is quickly moving toward the head of the pack in the race to develop the perfect artificial synapse. Researchers recently reported a string of advances at this week’s IEEE International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM 2022) and elsewhere, including ECRAM devices that use less energy, hold memory longer, and take up less space.
Complete article from IEEE Spectrum.
Explore
MIT Engineers Advance Toward a Fault-tolerant Quantum Computer
Adam Zewe | MIT News
Researchers achieved a type of coupling between artificial atoms and photons that could enable readout and processing of quantum information in a few nanoseconds.
Energy-Efficient and Environmentally Sustainable Computing Systems Leveraging Three-Dimensional Integrated Circuits
Wednesday, May 14, 2025 | 12:00 - 1:00pm ET
Hybrid
Zoom & MIT Campus
The Road to Gate-All-Around CMOS
Monday, April 14, 2025 | 10:00 AM to 11:00 AM
In-Person
Haus Room (36-428)
50 Vassar Street Cambridge, MA