April 30, 2025
In the future, quantum computers could rapidly simulate new materials or help scientists develop faster machine-learning models, opening the door to many new possibilities.
But these applications will only be possible if quantum computers can perform operations extremely quickly, so scientists can make measurements and perform corrections before compounding error rates reduce their accuracy and reliability.
The efficiency of this measurement process, known as readout, relies on the strength of the coupling between photons, which are particles of light that carry quantum information, and artificial atoms, units of matter that are often used to store information in a quantum computer.
Now, MIT researchers have demonstrated what they believe is the strongest nonlinear light-matter coupling ever achieved in a quantum system. Their experiment is a step toward realizing quantum operations and readout that could be performed in a few nanoseconds.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
MIDDAS: Memory Integration and Data Dis-Aggregation
Wednesday, November 19, 2025 | 12:00 - 1:00pm ET
Hybrid
Zoom & MIT Campus
Theory-Guided Strategy Expands the Scope of Measurable Quantum Interactions
Adam Zewe | MIT News
An oft-ignored effect can be used to probe an important property of semiconductors, a new study finds.
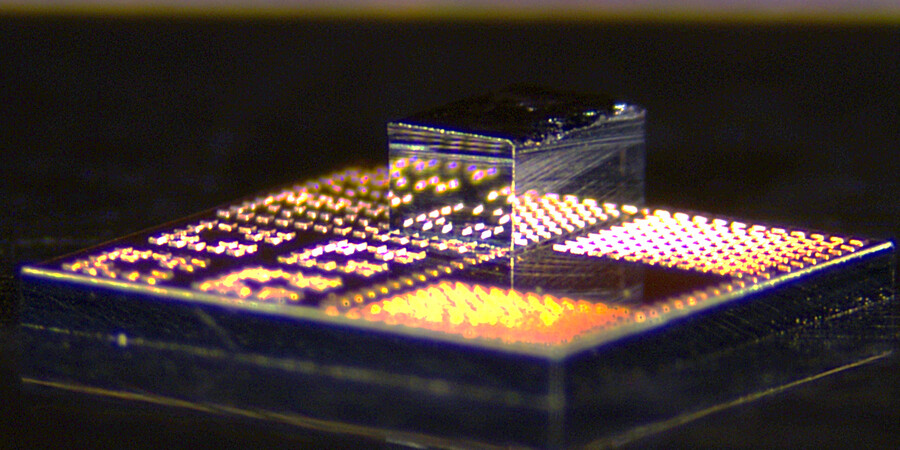
New 3D Chips could Make Electronics Faster and more Energy-Efficient
Adam Zewe | MIT News
The low-cost, scalable technology can seamlessly integrate high-speed gallium nitride transistors onto a standard silicon chip.