October 3, 2024
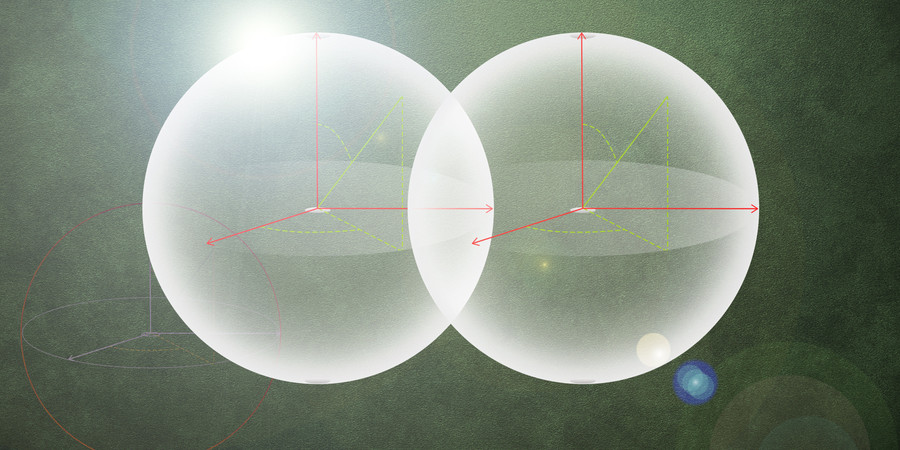
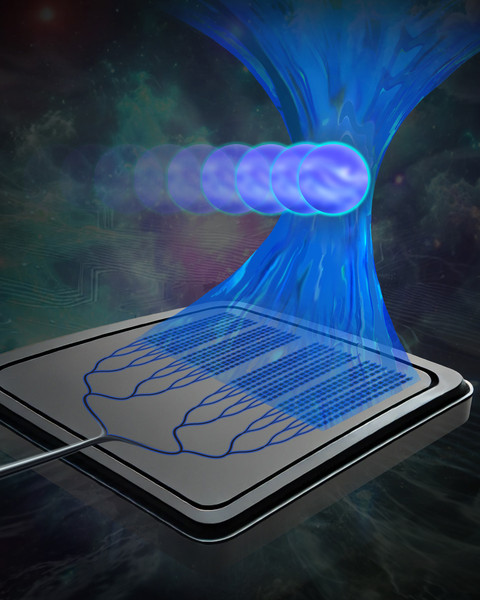
Small enough to fit in the palm of your hand, the device uses a beam of light emitted by a silicon-photonics chip to manipulate particles millimeters away from the chip surface. The light can penetrate the glass cover slips that protect samples used in biological experiments, enabling cells to remain in a sterile environment.
Traditional optical tweezers, which trap and manipulate particles using light, usually require bulky microscope setups, but chip-based optical tweezers could offer a more compact, mass manufacturable, broadly accessible, and high-throughput solution for optical manipulation in biological experiments.
However, other similar integrated optical tweezers can only capture and manipulate cells that are very close to or directly on the chip surface. This contaminates the chip and can stress the cells, limiting compatibility with standard biological experiments.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
MIT Engineers Advance Toward a Fault-tolerant Quantum Computer
Adam Zewe | MIT News
Researchers achieved a type of coupling between artificial atoms and photons that could enable readout and processing of quantum information in a few nanoseconds.
The Road to Gate-All-Around CMOS
Monday, April 14, 2025 | 10:00 AM to 11:00 AM
In-Person
Haus Room (36-428)
50 Vassar Street Cambridge, MA
2025 MIT AI Hardware Program Annual Symposium
Monday, March 31, 2025 | 10:00 AM - 3:30 PM ET
Multiple Speakers