Adam Zewe | MIT News Office
January 5, 2023
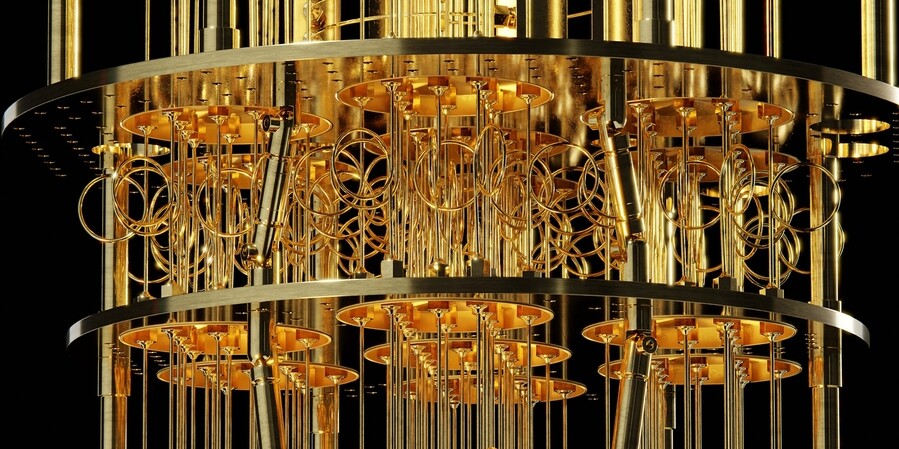
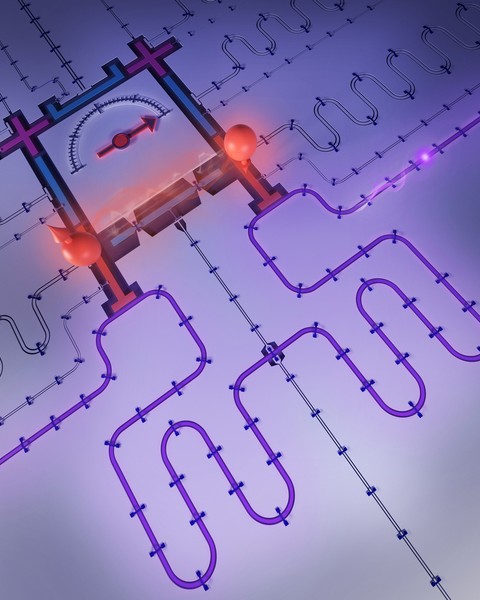
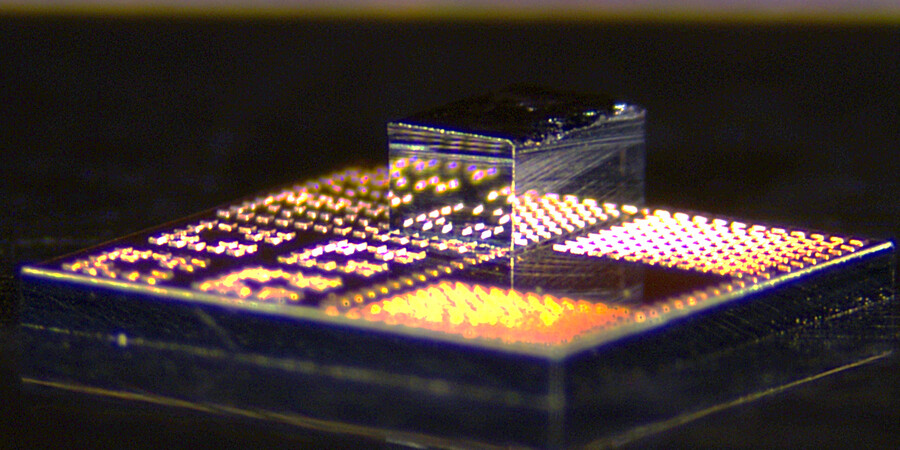
Quantum computers hold the promise of performing certain tasks that are intractable even on the world’s most powerful supercomputers. In the future, scientists anticipate using quantum computing to emulate materials systems, simulate quantum chemistry, and optimize hard tasks, with impacts potentially spanning finance to pharmaceuticals.
However, realizing this promise requires resilient and extensible hardware. One challenge in building a large-scale quantum computer is that researchers must find an effective way to interconnect quantum information nodes — smaller-scale processing nodes separated across a computer chip. Because quantum computers are fundamentally different from classical computers, conventional techniques used to communicate electronic information do not directly translate to quantum devices. However, one requirement is certain: Whether via a classical or a quantum interconnect, the carried information must be transmitted and received.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
New 3D Chips could Make Electronics Faster and more Energy-Efficient
Adam Zewe | MIT News
The low-cost, scalable technology can seamlessly integrate high-speed gallium nitride transistors onto a standard silicon chip.
Closing in on Superconducting Semiconductors
Julianna Mullen | Plasma Science and Fusion Center
Plasma Science and Fusion Center researchers created a superconducting circuit that could one day replace semiconductor components in quantum and high-performance computing systems.
Anantha Chandrakasan Named MIT Provost
Kathy Wren | MIT News
A faculty member since 1994, Chandrakasan has also served as dean of engineering and MIT’s inaugural chief innovation and strategy officer, among other roles.