Adam Zewe | MIT News Office
December 9, 2022
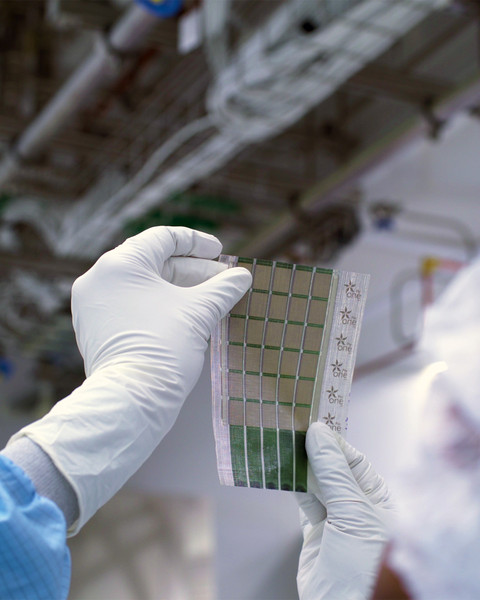
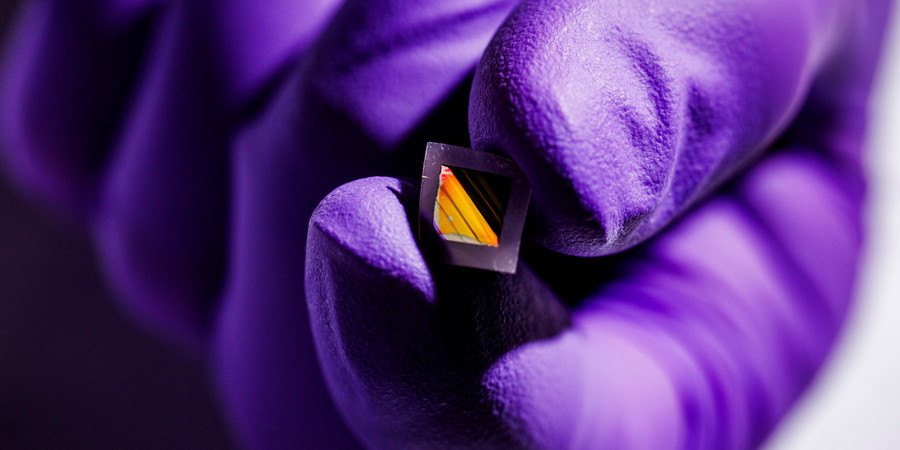
MIT engineers have developed ultralight fabric solar cells that can quickly and easily turn any surface into a power source.
These durable, flexible solar cells, which are much thinner than a human hair, are glued to a strong, lightweight fabric, making them easy to install on a fixed surface. They can provide energy on the go as a wearable power fabric or be transported and rapidly deployed in remote locations for assistance in emergencies. They are one-hundredth the weight of conventional solar panels, generate 18 times more power-per-kilogram, and are made from semiconducting inks using printing processes that can be scaled in the future to large-area manufacturing.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
III-Nitride Ferroelectrics for Integrated Low-Power and Extreme-Environment Memory
Monday, May 5, 2025 | 4:00 - 5:00pm ET
Hybrid
Zoom & MIT Campus
New Electronic “skin” could Enable Lightweight Night-vision Glasses
Jennifer Chu | MIT News
MIT engineers developed ultrathin electronic films that sense heat and other signals, and could reduce the bulk of conventional goggles and scopes.
MIT Engineers Print Synthetic “Metamaterials” that are Both Strong and Stretchy
Jennifer Chu | MIT News
A new method could enable stretchable ceramics, glass, and metals, for tear-proof textiles or stretchy semiconductors.