February 5, 2025
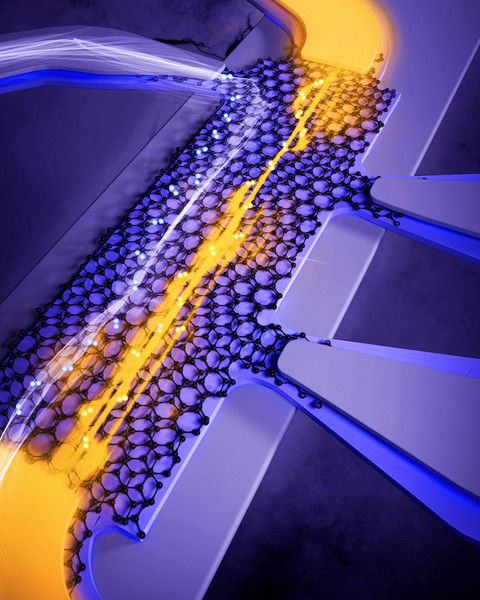
Superconducting materials are similar to the carpool lane in a congested interstate. Like commuters who ride together, electrons that pair up can bypass the regular traffic, moving through the material with zero friction.
But just as with carpools, how easily electron pairs can flow depends on a number of conditions, including the density of pairs that are moving through the material. This “superfluid stiffness,” or the ease with which a current of electron pairs can flow, is a key measure of a material’s superconductivity.
Physicists at MIT and Harvard University have now directly measured superfluid stiffness for the first time in “magic-angle” graphene — materials that are made from two or more atomically thin sheets of graphene twisted with respect to each other at just the right angle to enable a host of exceptional properties, including unconventional superconductivity.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
MIT Engineers Advance Toward a Fault-tolerant Quantum Computer
Adam Zewe | MIT News
Researchers achieved a type of coupling between artificial atoms and photons that could enable readout and processing of quantum information in a few nanoseconds.
New Chip Tests Cooling Solutions for Stacked Microelectronics
Kylie Foy | MIT Lincoln Laboratory
Preventing 3D integrated circuits from overheating is key to enabling their widespread use.
III-Nitride Ferroelectrics for Integrated Low-Power and Extreme-Environment Memory
Monday, May 5, 2025 | 4:00 - 5:00pm ET
Hybrid
Zoom & MIT Campus