MIT Engineers Develop a Way to Determine how the Surfaces of Materials Behave
David L. Chandler | MIT News
Using machine learning, the computational method can provide details of how materials work as catalysts, semiconductors, or battery components.
New Study Shows how Universities are Critical to Emerging Fusion Industry
Peter Reuell | Julianna Mullen | Plasma Science and Fusion Center
Fusion’s success as a renewable energy depends on the creation of an industry to support it, and academia is vital to that industry’s development.
With a Quantum “Squeeze,” Clocks Could Keep Even More Precise Time, MIT Researchers Propose
Jennifer Chu | MIT News
Clocks, lasers, and other oscillators could be tuned to super-quantum precision, allowing researchers to track infinitesimally small differences in time, and measure quantum phenomena, including the presence of dark matter.
Celebrating five years of MIT.nano
Amanda Stoll DiCristofaro | MIT.nano
The Nano Summit highlights nanoscale research across multiple disciplines at MIT.
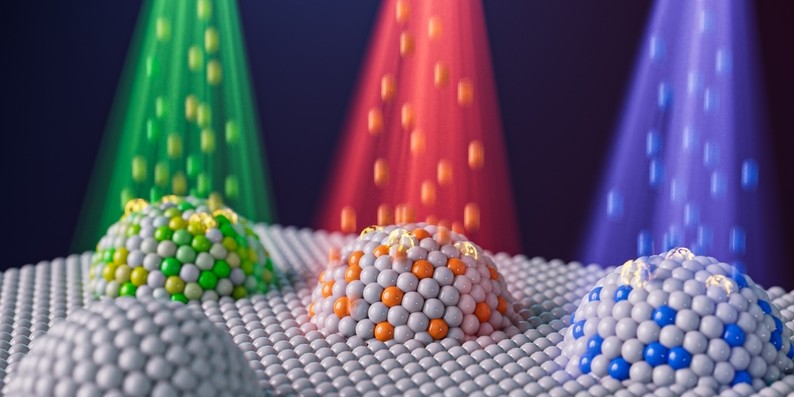
Team Engineers Nanoparticles Using Ion Irradiation to Advance Clean Energy and Fuel Conversion
Elizabeth Thomson | Materials Research Laboratory
Combining the techniques, metal exsolution and ion irradiation, demonstrates control over key nanoparticle properties leading to better performance.
Engineers Develop an Efficient Process to Make Fuel from Carbon Dioxide
David L. Chandler | MIT News
The approach directly converts the greenhouse gas into formate, a solid fuel that can be stored indefinitely and could be used to heat homes or power industries.
Morris Chang ’52, SM ’53 describes the secrets of semiconductor success
Peter Dizikes | MIT News
At MIT, a driving force in the chip-making industry discusses the rise of TSMC and Taiwan as a manufacturing center.
Making More Magnetism Possible with Topology
Peter Reuell | Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering
MIT researchers show how topology can help create magnetism at higher temperatures.
Quantum Repeaters Use Defects in Diamond to Interconnect Quantum Systems
Ariana Tantillo | MIT Lincoln Laboratory
This technology for storing and transmitting quantum information over lossy links could provide the foundation for scalable quantum networking.
Sensing and Controlling Microscopic Spin Density in Materials
David L. Chandler | MIT News
By fine-tuning the spin density in some materials, researchers may be able to develop new quantum sensors or quantum simulations.