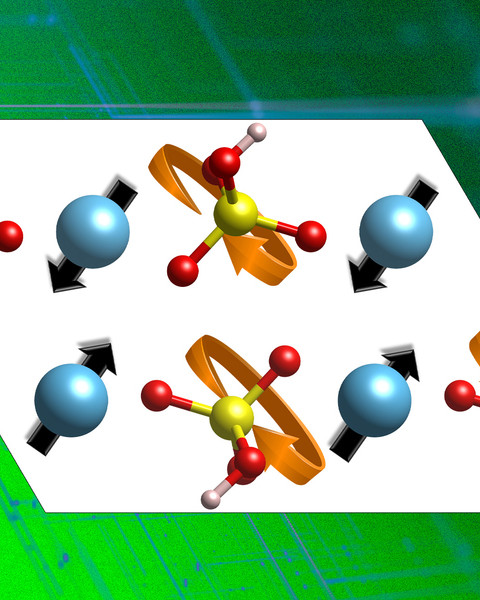
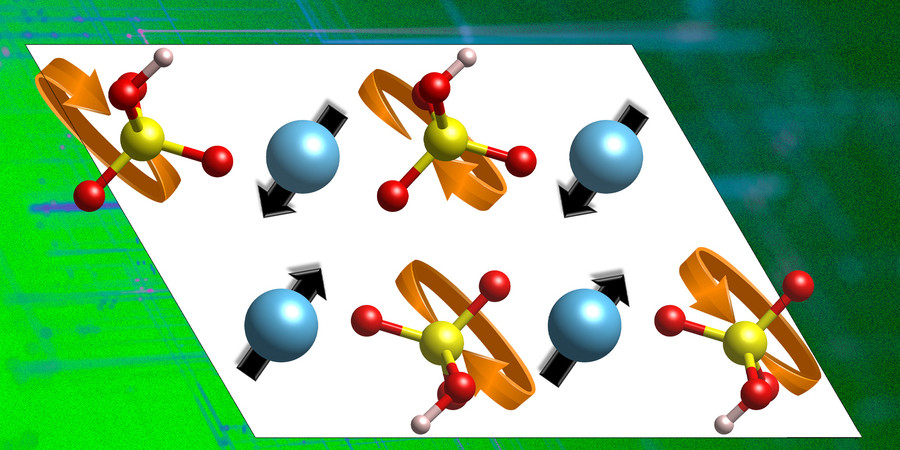
Proton-conducting Materials could Enable New Green Energy Technologies
David L. Chandler | MIT News
Analysis and materials identified by MIT engineers could lead to more energy-efficient fuel cells, electrolyzers, batteries, or computing devices.
Physicists Create Five-lane Superhighway for Electrons
Elizabeth A. Thomson | Materials Research Laboratory
Work on the superhighway for electrons that can occur in rhombohedral graphene, a special kind of graphite, could lead to ultra-efficient electronics and more.
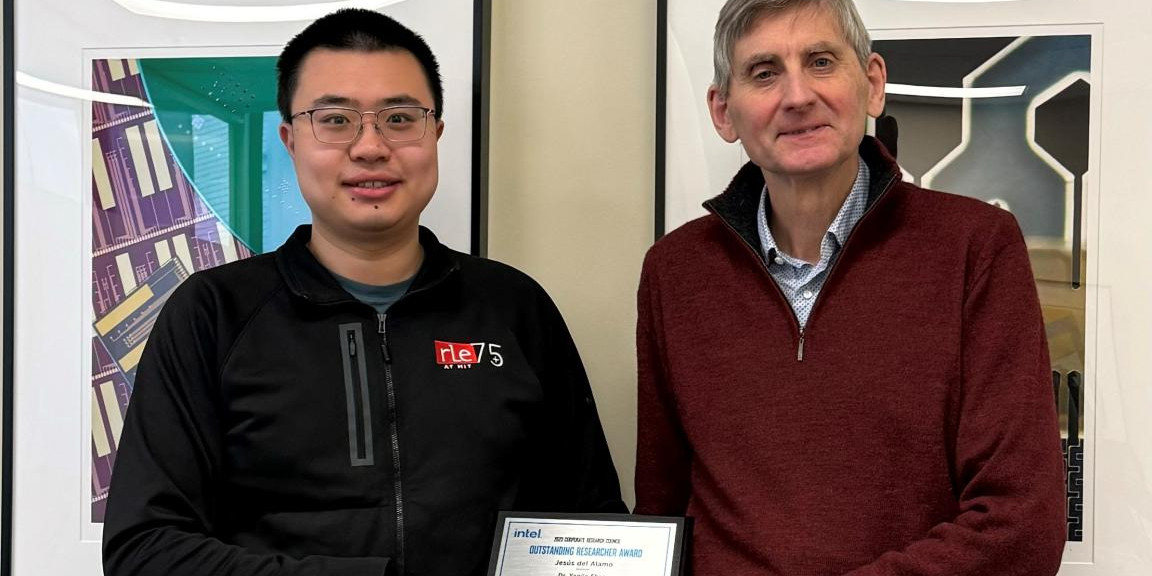
Yanjie Shao and Jesús del Alamo receive Intel’s 2023 Outstanding Researcher Award
Microsystems Technology Laboratories
They were selected for this award for their work on “Exploring the Limits of Vertical-Nanowire Tunnel Field-Effect Transistors in the Nanoscale.”
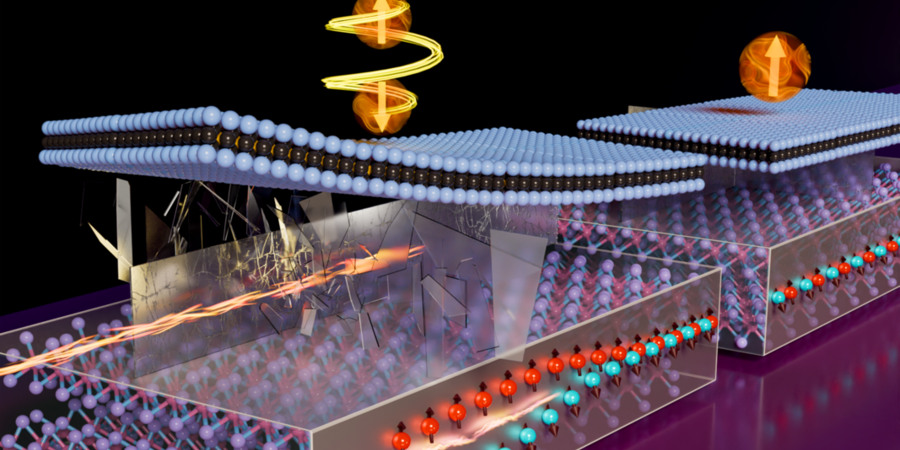
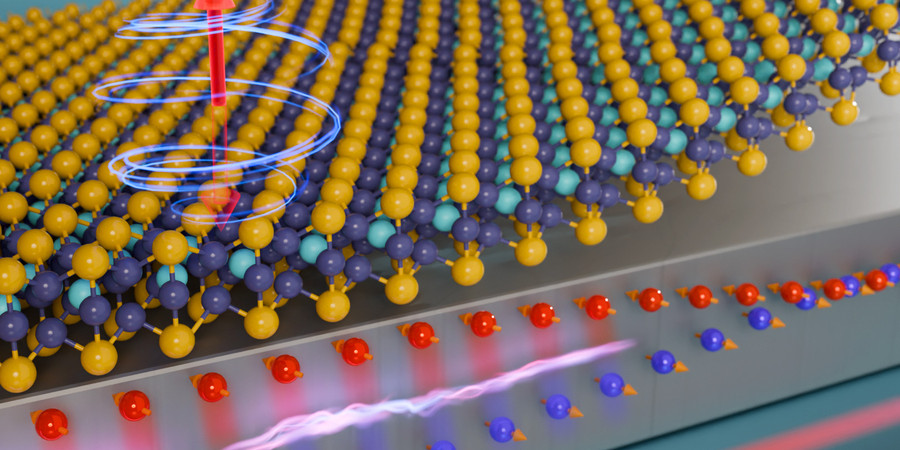
Propelling Atomically Layered Magnets Toward Green Computers
Media Lab
MIT scientists have tackled key obstacles to bringing 2D magnetic materials into practical use, setting the stage for the next generation of energy-efficient computers.
Researchers Harness 2D Magnetic Materials for Energy-efficient Computing
Adam Zewe | MIT News
An MIT team precisely controlled an ultrathin magnet at room temperature, which could enable faster, more efficient processors and computer memories.
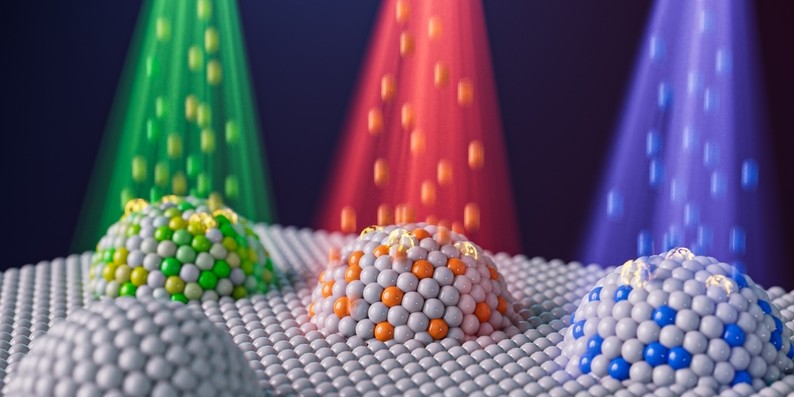
Team Engineers Nanoparticles Using Ion Irradiation to Advance Clean Energy and Fuel Conversion
Elizabeth Thomson | Materials Research Laboratory
Combining the techniques, metal exsolution and ion irradiation, demonstrates control over key nanoparticle properties leading to better performance.
Analog In-Memory Computing for Deep Learning Inference
Wednesday, November 15, 2023 | 12:00 - 1:00pm ET
Hybrid
Grier A (34-401A)
50 Vassar Street Cambridge, MA
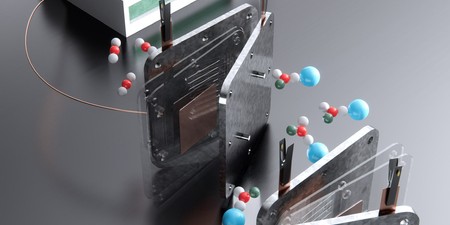
Engineers Develop an Efficient Process to Make Fuel from Carbon Dioxide
David L. Chandler | MIT News
The approach directly converts the greenhouse gas into formate, a solid fuel that can be stored indefinitely and could be used to heat homes or power industries.
Accelerating AI Tasks While Preserving Data Security
Adam Zewe | MIT News
The SecureLoop search tool efficiently identifies secure designs for hardware that can boost the performance of complex AI tasks, while requiring less energy.
System Combines Light and Electrons to Unlock Faster, Greener Computing
Alex Shipps | MIT CSAIL
“Lightning” system connects photons to the electronic components of computers using a novel abstraction, creating the first photonic computing prototype to serve real-time machine-learning inference requests.